History of Storage Devices
A Storage Device is a piece of computer equipment on which information can be stored.
Types of Storage
There are four type of storage:


Optical Disc
• Optical disc is any storage media that holds content in digital format and is read using a laser assembly is considered optical media.
• The most common types of optical media are
– Blu-ray (BD)
– Compact Disc (CD)
– Digital Versatile Disc (DVD)
Types of Storage
There are four type of storage:
• Primary Storage
• Secondary Storage
• Tertiary Storage
• Off-line Storage
Primary Storage
• Also known as main memory.
• Also known as main memory.
• Main memory is directly or indirectly connected to the central processing unit via a memory bus.
• The CPU continuously reads instructions stored there and executes them as required.
• Example: – RAM – ROM – Cache
RAM
• It is called Random Access Memory because any of the data in RAM can be accessed just as fast as any of the other data.
• It is called Random Access Memory because any of the data in RAM can be accessed just as fast as any of the other data.
• There are two types of RAM:
– DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
– SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
Static RAM

• Faster
• More expensive
• More power consumption
• does not need to be refreshed
Dynamic RAM

• Slower
• Less expensive
• Less power consumption
• needs to be refreshed thousands of times per second
ROM
• This memory is used as the computer begins to boot up.
• This memory is used as the computer begins to boot up.
• Small programs called firmware are often stored in ROM chips on hardware devices (like a BIOS chip), and they contain instructions the computer can use in performing some of the most basic operations required to operate hardware devices.
• ROM memory cannot be easily or quickly overwritten or modified.
Cache
• Cache is a high-speed access area that can be either a reserved section of main memory or a storage device.
• Cache is a high-speed access area that can be either a reserved section of main memory or a storage device.
• Most computers today come with L3 cache or L2 cache, while older computers included only L1 cache.
Secondary Storage
• It is not directly accessible by the CPU.
• Computer usually uses its input/output channels to access secondary storage and transfers the desired data using intermediate area in primary storage.
• Example: – Hard disk
Hard Disk
• The hard disk drive is the main, and usually largest, data storage device in a computer.
• It can store anywhere from 160 gigabytes to 2 terabytes.
• Hard disk speed is the speed at which content can be read and written on a hard disk.
• A hard disk unit comes with a set rotation speed varying from 4500 to 7200 rpm.
• Disk access time is measured in milliseconds.
Internal Hard Disk External Hard Disk
Portability → No Portability → Yes
Price → Less Expensive Price →More Expensive
Speed → Fast Speed →Slow
Size → Big Size →Small
Tertiary Storage
• Typically it involves a robotic mechanism which will mount (insert) and dismount removable mass storage media into a storage device.
• It is a comprehensive computer storage system that is usually very slow, so it is usually used to archive data that is not accessed frequently.
• This is primarily useful for extraordinarily large data stores, accessed without human operators.
Tertiary Storage
• Examples:
• Examples:
– Magnetic Tape
– Optical Disc
Magnetic Tape
• A magnetically coated strip of plastic on which data can be encoded.
• A magnetically coated strip of plastic on which data can be encoded.
• Tapes for computers are similar to tapes used to store music.
• Tape is much less expensive than other storage mediums but commonly a much slower solution that is commonly used for backup.
Optical Disc
• Optical disc is any storage media that holds content in digital format and is read using a laser assembly is considered optical media.
• The most common types of optical media are
– Blu-ray (BD)
– Compact Disc (CD)
– Digital Versatile Disc (DVD)
CD DVD BD
Capacity 700MB 4.7GB – 17GB 50GB
Wavelength 780nm 650nm 405nm
Read/Write Speed 1200KB/s 10.5MB/s 36MB/s
Off-line Storage
• Also known as disconnected storage.
• Also known as disconnected storage.
• Is a computer data storage on a medium or a device that is not under the control of a processing unit.
• It must be inserted or connected by a human operator before a computer can access it again.
• Also known as disconnected or removable storage.
• Is a computer data storage on a medium or a device that is not under the control of a processing unit.
• It must be inserted or connected by a human operator before a computer can access it again.
• Examples:
– Floppy Disk
– Zip diskette
– USB Flash drive
– Memory card
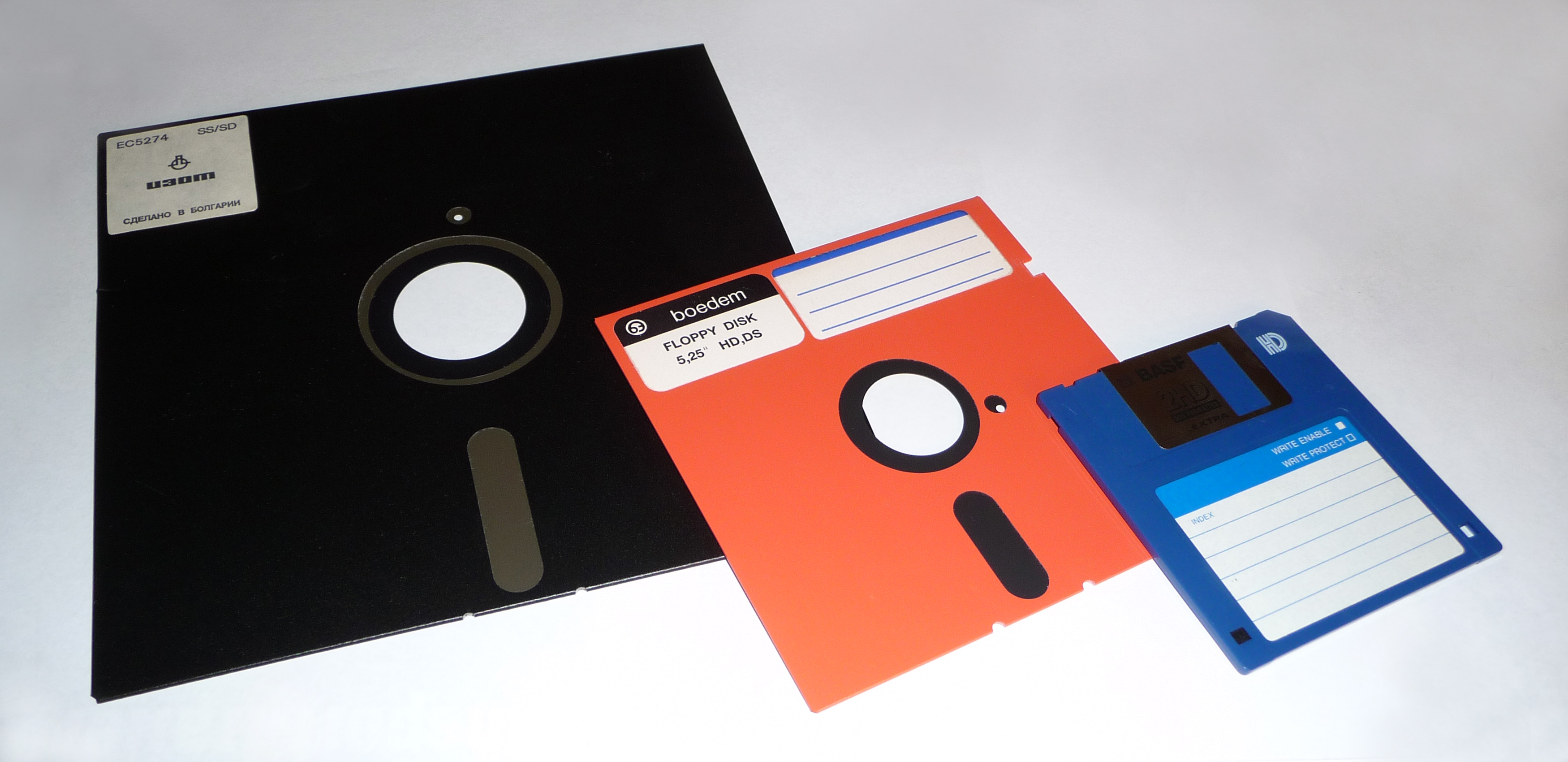
Floppy Disk
• A soft magnetic disk.
• A soft magnetic disk.
• Floppy disks are portable.
• Floppy disks are slower to access than hard disks and have less storage capacity, but they are much less expensive.
• Can store data up to 1.44MB.
• Two common sizes: 5 ¼” and 3 ½”.

Zip Diskette
• Hardware data storage device developed by Iomega that functions like a Standard 1.44" floppy drive.
• Hardware data storage device developed by Iomega that functions like a Standard 1.44" floppy drive.
• Capable to hold up to 100 MB of data or 250 MB of data on new drives.
• Now it less popular as users needed larger storage capabilities.
USB Flash Drive
• A small, portable flash memory card that plugs into a computer’s USB port and functions as a portable hard drive.
• A small, portable flash memory card that plugs into a computer’s USB port and functions as a portable hard drive.
• Flash drives are available in sizes such as 256MB, 512MB, 1GB, 5GB, and 16GB and are an easy way to transfer and store information.
Memory Card
• An electronic flash memory storage disk commonly used in consumer electronic devices such as digital cameras, MP3 players, mobile phones, and other small portable devices.
• An electronic flash memory storage disk commonly used in consumer electronic devices such as digital cameras, MP3 players, mobile phones, and other small portable devices.
• Memory cards are usually read by connecting the device containing the card to your computer, or by using a USB card reader.
History
- Punch cards were the first effort at Data Storage in a machine language. Punch cards were used to communicate information to equipment "before" computers were developed. The punched holes originally represented a sequence of instructions for a piece of equipment, such as textile looms. Basile Bouchon developed the punch card as a control for looms in 1725.
One of these technologies was the first memory disk called the floppy disk invented by Alan Shugart at IBM in 1971

The Selectron Tube
The Selectron tube had a capacity of 256 to 4096 bits (32 to 512 bytes). The 4096-bit Selectron was 10 inches long and 3 inches wide. Originally developed in 1946, the memory storage device proved expensive and suffered from production problems, so it never became a success.

Punch Cards
Early computers often used punch cards for input both of programs and data. Punch cards were in common use until the mid-1970s. It should be noted that the use of punch cards predates computers. They were used as early as 1725 in the textile industry (for controlling mechanized textile looms).

Punched Tape
Same as with punch cards, punched tape was originally pioneered by the textile industry for use with mechanized looms. For computers, punch tape could be used for data input but also as a medium to output data. Each row on the tape represented one character.

Magnetic Drum Memory
Invented all the way back in 1932 (in Austria), it was widely used in the 1950s and 60s as the main working memory of computers. In the mid-1950s, magnetic drum memory had a capacity of around 10 kB.

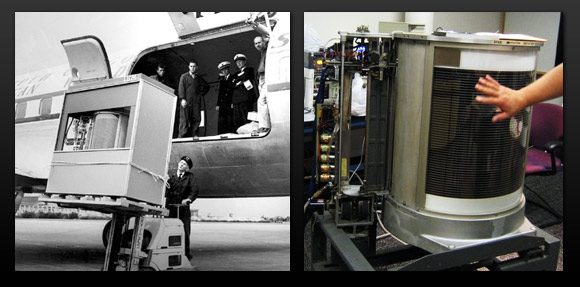




The Hard Disk Drive
The first hard disk drive was the IBM Model 350 Disk File that came with the IBM 305 RAMAC computer in 1956. It had 50 24-inch discs with a total storage capacity of 5 million characters (just under 5 MB).

The first hard drive to have more than 1 GB in capacity was the IBM 3380 in 1980 (it could store 2.52 GB). It was the size of a refrigerator, weighed 550 pounds (250 kg), and the price when it was introduced ranged from $81,000 to $142,400.
The Laserdisc
We mention it here mainly because it was the precursor to the CD-ROM and other optical storage solutions. It was mainly used for movies. The first commercially available laserdisc system was available on the market late in 1978 (then called Laser Videodisc and the more funkily branded DiscoVision) and were 11.81 inches (30 cm) in diameter. The discs could have up to 60 minutes of audio/video on each side. The first laserdiscs had entirely analog content. The basic technology behind laserdiscs was invented all the way back in 1958.

The Floppy Disc
The diskette, or floppy disk (named so because they were flexible), was invented by IBM and in common use from the mid-1970s to the late 1990s. The first floppy disks were 8 inches, and later in came 5.25 and 3.5-inch formats. The first floppy disk, introduced in 1971, had a capacity of 79.7 kB, and was read-only. A read-write version came a year later.

Magnetic Tape
Magnetic tape was first used for data storage in 1951. The tape device was called UNISERVO and was the main I/O device on the UNIVAC I computer. The effective transfer rate for the UNISERVO was about 7,200 characters per second. The tapes were metal and 1200 feet long (365 meters) and therefore very heavy.

No comments:
Post a Comment